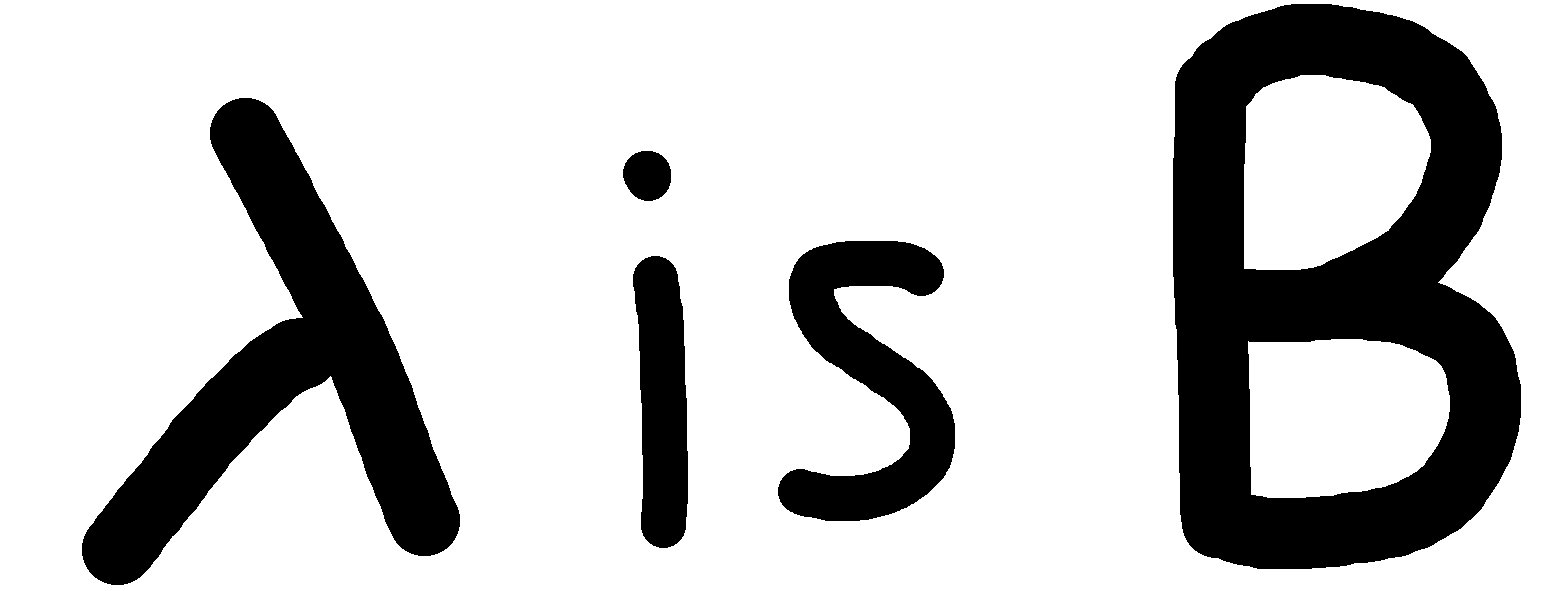Equality
lisb=> (= 1 1) ;; B: 1=1
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (not= 1 1) ;; B: 1/=1
nil ;; FALSE
Logical Connectives
Negation
lisb=> (not (= 1 2)) ;; B: not(1=2)
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
Binary operators
lisb=> (and (= 1 1) (= 2 2)) ;; B: 1=1 & 2=2
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (or (= 1 2) (= 2 2)) ;; B: 1=2 or 2=2
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
The implication and equivalence have an alias each:
lisb=> (=> (= 1 2) (= 1 1)) ;; B: 1=2 => 1=1
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (implication (= 1 2) (= 1 1)) ;; B: 1=2 => 1=1
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (<=> (= 1 2) (= 1 1)) ;; B: 1=2 <=> 1=1
nil ;; FALSE
lisb=> (equivalence (= 1 2) (= 1 1)) ;; B: 1=2 <=> 1=1
nil ;; FALSE
Quantifiers
In B, the universal quantification requires an implication in the body. In lisb, you can keep this style, or just use two arguments for the premise and the conclusion. It is automatically re-written.
lisb=> (for-all [:x] (=> (member? :x nat1-set) (< 0 :x))) ;; B: !(x).(x:NAT1 => 0 < x)
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (for-all [:x] (member? :x nat1-set) (< 0 :x)) ;; B: !(x).(x:NAT1 => 0 < x)
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (exists [:x] (< :x 10)) ;; B: #(x).(x < 10)
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (exists [:x :y] (< :x 10 :y)) ;; B: #(x,y).(x < 10 & 10 < y)
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
Conversion to Boolean
lisb=> (pred->bool (= 1 1)) ;; B: bool(1=1)
{} ;; TRUE, no bindings
lisb=> (pred->bool (= 1 2)) ;; B: bool(1=2)
nil ;; FALSE